Introduction
Studying isn’t just for students. Professionals, entrepreneurs, and lifelong learners all need effective learning habits. Yet some people grow rapidly while others forget quickly. The difference lies in study methods. This guide shares proven, practical techniques to boost learning efficiency and retention.
1. Why Study Methods Matter
- Efficiency: effective methods can double or triple results
- Consistency: enjoyment and achievement sustain long-term learning
- Application: true learning means applying knowledge, not just memorizing
👉 It’s not about “how long you study,” but “how you study.”

2. The Power of Goal Setting
- Short-term: weekly tests, project research
- Mid-term: certifications, skill improvement
- Long-term: career growth, fluency in new languages
💡 Clear goals fuel stronger motivation and direction.
3. Effective Learning Strategies
- Spaced Repetition: spread sessions out (e.g., 1 hour/day × 3 days > 3 hours in one day)
- Active Recall: test yourself instead of rereading
- Interleaving: mix subjects for deeper understanding
- Feedback: review errors quickly using mentors, apps, or study groups
4. Boosting Focus with Environment
- Quiet, clutter-free study space
- Block distractions (apps, SNS)
- Separate work & rest time clearly
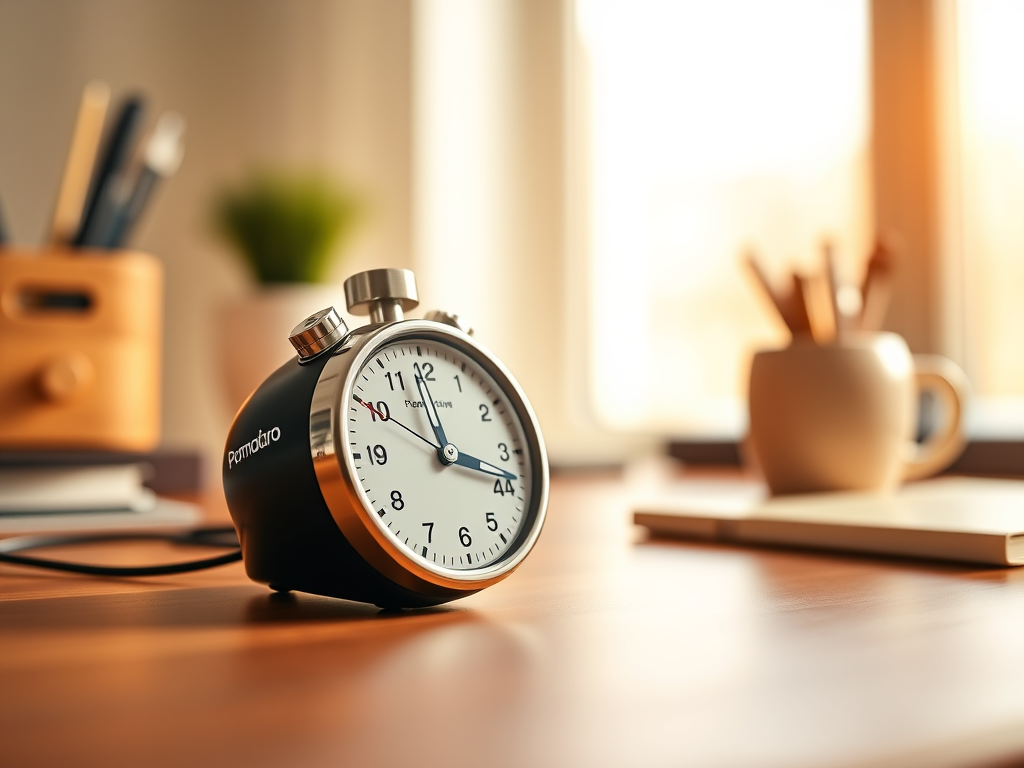
- Use Pomodoro (25 min focus + 5 min break)
5. Organizing Study Materials
- Notes: focus on summaries & diagrams, not copying
- Mind maps: link concepts visually
- Flashcards: perfect for vocabulary & definitions (digital apps available)
👉 The process of organizing improves memory more than re-reading.
6. Building Self-Directed Study Habits
- Set a fixed daily study time
- Small daily goals (e.g., 20 words, 10 problems)
- Check completed tasks for motivation
- Track progress with long-term study plans
7. Balancing Study & Rest
- Take short walks or stretch to refresh
- Sleep well to consolidate memory
- Enjoy hobbies to stimulate different brain areas
⚖️ Learning thrives on rhythm: focus + rest.
8. Learning in the Digital Era
- Platforms: Coursera, Udemy, Inflearn
- Content: YouTube, blogs
- AI tools: chatbots, translators, summarizers
👉 Be selective—filter reliable sources to avoid information overload.
Conclusion
Effective learning isn’t about cramming—it’s about a cycle: Goal → Plan → Action → Review → Apply. Start today by setting clear goals and practicing active recall. With small, consistent changes, you’ll learn faster, retain longer, and grow into a smarter learner.